
We could have borrowed from Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s “Love in the time of cholera” to title this piece, “Oil and gas in the time of coronavirus”. But that would only recognize the coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) for its Black Swan impact on oil demand and ignore the supply shock posed by Russia’s refusal to hyphenate itself with OPEC again in cutting oil production. Broader uncertainties from an election year in the U.S. and growing investor clamor for shale profitability and energy transition initiatives add further, even if now less urgent, uncertainties.
We at ADI instead see the “perfect storm” as a better metaphor for the collective impact from the Russian-Saudi spat and COVID-19. Metaphors and clever writing aside, how should we think about this perfect storm? We try to address this here with our firm’s research and consulting work.
Why are we here?
The oil markets – led by Saudi and OPEC through the majors and the shale operators to the traders and analysts – were blindsided by Russia’s refusal to cut oil production with OPEC in an year when oil demand growth was expected to decline independent of the coronavirus.
Russia made some noise about OPEC cheating on its commitments but abandoned its three-year alliance with OPEC primarily to harm U.S. shale supply, which has been, as such, constrained by rising investor disenchantment. Larger geopolitical reasons such as U.S. sanctions on Rosneft and Nord Stream 2 also motivated Russia which is today in a stronger economic position relative to the 2014 oil price crash.
Surveying the damage
Unwilling to lose market share and also force Russia to return to negotiations, Saudi announced plans to raise production from 9.7 million barrels per day (bpd) to 12.3 million bpd starting April 2020. It also doubled down on its bet by offering discounts of $4 to $8 per barrel on its production. In solidarity, the United Arab Emirates will increase supply by 0.8 million bpd.
Russia plans to increase production too but only by 0.5 million bpd as it is limited by sanctions on its oil trading. In addition, incremental supply growth may come from Libya once the outage there ends along with some small production growth in other places.
At this rate, collectively, the market in 2020 will be oversupplied by 3-5 million bpd and global inventory will surpass 400 million barrels over the next few months (see Exhibit 1 for one scenario variant).
Exhibit 1. Global crude oil supply-demand scenario, million bpd.
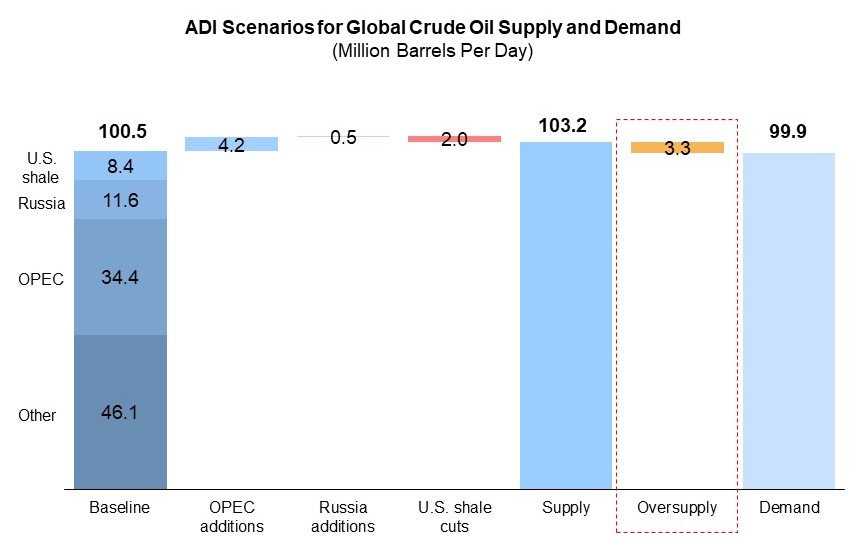
However, two reasons make estimating this supply-demand balance difficult.
- Oil demand destruction from COVID-19 is highly uncertain and today ranges from 0.6 to 1.2 million bpd for all of 2020. First quarter oil demand alone likely fell more than 3.5 million bpd led by lockdowns in China that are spreading rapidly to U.S. and Europe. Peak demand slump estimates range even more wildly from 3.5 million bpd to as much as 10 million bpd likely peaking in the second quarter of 2020.
- Operators will cut production as oil prices plumb new depths – Brent was below $25 a barrel on March 18 and WTI barely at $20 – but the extent is uncertain. But we do know that most of those supply cuts will likely happen in the U.S. Acknowledging their role as swing producers, publicly-listed shale operators have started cutting capital spending with most reductions averaging 25% to 35% (see Exhibit 2).
Exhibit 2. Capex cuts by shale players in 1Q 2020, USD million.

Worryingly enough, corresponding production cuts are small for those who have disclosed those details suggesting that operators may be trimming drilling but will continue completing their well inventories limiting the supply impact. The last oil price crash was followed by supply cuts that exceeded 1 million bpd over 15 months beginning in late 2014. The shale industry will need to deliver much deeper cuts this time – think around 2 million bpd through 2020 as opposed to growth forecasts of 0.6 to 0.9 million bpd – in order to keep oil prices from falling and staying at marginal cash costs.
ADI is developing scenarios of oil & gas impacts from COVID-19 and the oil price crash. The report will include granular forecasts for upstream (shale and offshore), midstream (gas processing, NGLs, and pipelines), LNG, refining, and petchem. Download prospectus, and contact us at info@adi-analytics.com to learn more.
What happens now?
ADI has developed three scenarios (see Exhibit 3 and 4) of what may happen going forward.
Exhibit 3. ADI crude oil price scenario descriptions.

- “Recession” is our most pessimistic outlook where oil demand suffers a protracted slump as the global economy slips into a recession as COVID-19 lockdowns spread and persist through the summer of 2020. Oil prices will test new lows and stay close to the marginal cash cost of $10 to $15 a barrel through most of 2020. They will rise slowly to $25 a barrel in 2022, just barely above the marginal cash costs. There will most likely be government stimuli as well as a deal between Russia and OPEC but they will be irrelevant as the damage will be too severe.
- “Reconciliation” is where we forecast a moderate level of pessimism around the global economy, COVID-19, and oil prices, which hover in the low $30s a barrel in 2020 and rise up to low- to mid-$40s by 2022. In this world, we stay at the current or slightly expanded levels of regional lockdowns, Russia and OPEC don’t do a deal until June, and government stimuli help avoid a recession but the world slips into an economic slowdown.
- “Rebound” is our most optimistic scenario, given the current situation, where oil prices attain high $30s a barrel in 2020 and rise up to $45 to $55 a barrel in 2022. A lot of things need to come together for this scenario to pass. The current set of lockdowns do not spread and they and COVID-19 blow over through the spring, Russia and OPEC come to a deal in the next month or two, and government stimuli prove to be highly effective and support an economic rebound. Even so, the aftershocks from COVID-19 and the Russia-OPEC spat linger through larger oil inventories and lead to low oil prices in the near- to mid-term.
Exhibit 4. ADI crude oil price scenarios, Brent, USD per barrel.

ADI is developing scenarios of oil & gas impacts from COVID-19 and the oil price crash. The report will include granular forecasts for upstream (shale and offshore), midstream (gas processing, NGLs, and pipelines), LNG, refining, and petchem. Download prospectus, and contact us at info@adi-analytics.com to learn more.
So what?
None of these scenarios will come to pass as forecasted. But a number of implications recur across our three scenarios, and the oil and gas industry may consider paying attention to them.
- Oil and gas companies should prepare for an average oil price of $20 to $30 a barrel for 2020. Modest improvements will come in 2021 with recovery only in 2022.
- There is limited upside for oil prices through most of 2020 unless Russia and OPEC agree to a deal within the next several weeks. As Saudi Arabia ramps up production, the global oil inventory will surge and any price rise will have to wait until those inventories are depleted. Further, nearly two-thirds of U.S. shale production has been hedged at ~$55 a barrel for 2020 and is unlikely to fall at current prices.
- Russia and Saudi Arabia both have sufficient financial resources to weather a protracted period of low oil prices. This limits the probability of a deal in the near term.
- U.S. shale production will fall – only by how much is up for debate. Even if hedges protect U.S. shale operators through 2020, sharp cuts will come in 2021. Unlike the oil price crash of 2014-16, there is limited private equity appetite to buy distressed operators. As a result, operators that are small or hold undifferentiated acreage will face significant distress.
- North American natural gas producers will be an unlikely beneficiary of this oil price crash. As light tight oil supply falls so will associated gas production, which has driven over 50% of gas supply growth in North America in recent years. This reduction in the growth of gas supply should help Henry Hub pricing.
- However, some of this will be limited by caps on natural gas demand growth that will come from delays to the second wave of LNG export projects in the U.S.
- Refiners’ have gone from starry dreams of a “golden year” thanks to IMO 2020 to a nightmare scenario of cutting refinery runs as refined product demand grinds to a crushing halt due to COVID-19 lockdowns around the world. Downstream companies with complex refineries, strong linkages to export markets, mature commercial trading teams, and integrated petrochemical assets will weather through these times but other refiners will struggle.
- Midstream companies will face challenges with product exports, in particular, light tight oil, which will have to be discounted extensively to find overseas buyers. Support for existing and new capital projects will, of course, decline. Finally, we anticipate investor flight to quality based on contract portfolios.
- Traders and majors with strong commercial organizations will likely benefit across at least two scenarios – “reconciliation” and “rebound” – with limited prospects in the “recession” scenario.
- Shipping and logistics players with tankers, terminals, product storage tanks, and blending capabilities may benefit in this environment as a contango market drives interest and demand for storage.
ADI is developing scenarios of oil & gas impacts from COVID-19 and the oil price crash. The report will include granular forecasts for upstream (shale and offshore), midstream (gas processing, NGLs, and pipelines), LNG, refining, and petchem. Download prospectus, and contact us at info@adi-analytics.com to learn more.




















