
Over the past few decades, the buzz surrounding nuclear energy has subsided significantly. One of the primary reasons for this downturn is the public memory of catastrophic incidents like Fukushima and Chernobyl which have only further entrenched the perception that nuclear energy is risky. Additionally, the escalating total costs and construction schedule delays associated with running nuclear power plants, which have made it an unattractive choice for many investors. However, a new technological breakthrough known as Small Modular Reactors (SMR) promises to revolutionize the field, promising safer, cleaner and cost-effective nuclear energy. SMRs offer a compact, safer, and more economically viable approach to nuclear energy, presenting the promise of sustainable, high-capacity power generation in a rapidly growing energy sector.
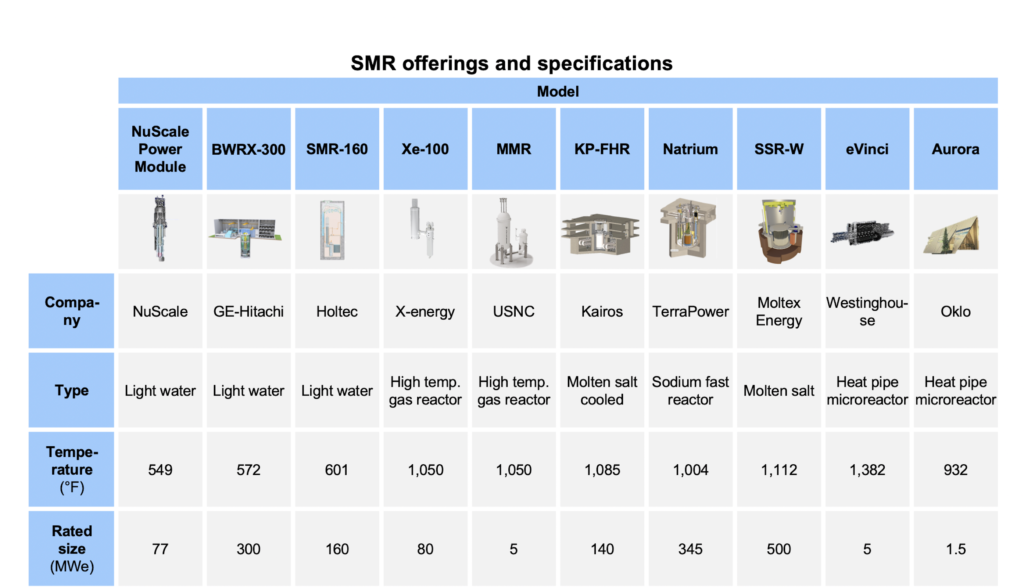
After recently reviewing the SMR market, ADI categorized the various models on offer based on their operational efficiency, technological advancement and current market status (See Figure 1). Notably, NuScale’s SMR emerged as a leading contender. With a pressurized water reactor configuration, this model operates at a standard temperature of around 549 °F and boasts a modest but efficient size of 77 MWe. It also possesses the significant milestone of Design Certification granted by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), indicating it’s readiness for commercial deployment.
SMRs are characterized by their reduced size compared to traditional nuclear reactors. This compactness offers numerous benefits. Firstly, the design and construction of SMRs are conducted in factories, with completed modules transported to their final installation site. This process reduces construction times and costs, leading to shorter lead times and making nuclear projects more manageable and less financially burdensome.
Another major advantage is the scalability of SMRs. The modularity of these reactors allows for incremental additions of power generation capacity as and when needed. This feature offers a flexibility that is not available with traditional nuclear reactors, and it significantly improves the economic viability of nuclear projects by matching investment closely with demand.
In the realm of safety, SMRs represent a significant advancement. Thanks to their smaller size and innovative designs, SMRs rely heavily on passive safety systems that require little to no human intervention. Moreover, the lower quantities of nuclear fuel in each module result in reduced potential risks in case of accidents.
Economically, SMRs demonstrate competitive potential. The modular construction and scalability reduce capital costs and financial risks, thereby making nuclear energy an attractive option for a wider range of investors and markets. By decreasing the financial entry barriers, SMRs could lead to a broader adoption of nuclear power, especially in developing countries or remote regions where large-scale nuclear plants are not feasible.
In the rapidly shifting energy landscape, SMRs are garnering attention for their potential to enhance energy security, a critical issue underlined by the recent conflict between Russia and Ukraine. The decentralized nature of SMRs allows for a distribution of power sources that mitigates the vulnerabilities of relying on a limited number of large-scale plants. In the context of Europe, which has been significantly impacted by the geopolitical tensions, the deployment of SMRs could offer a strategic solution to diversify energy supplies, reduce reliance on external energy imports, and ensure continuous, uninterrupted power generation.
The potential of SMRs, however, is not solely in their ability to provide a stable energy supply. An essential piece of the puzzle resides in economic policy, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). This legislation is designed to stimulate investment for clean energy solutions, subsequently creating a more favorable financial environment for the development and implementation of innovative technologies like SMRs.
Under the provisions of the IRA, substantial financial incentives could be extended to initiatives championing the deployment of clean energy technologies, such as SMRs. By offsetting the initial capital costs and minimizing the financial risks associated with nuclear projects, the IRA serves to boost the economic viability of SMRs, encouraging increased investment and acceleration in their adoption.
A noteworthy feature of SMRs is their ability to utilize excess heat for the storage of electricity, thus enhancing overall efficiency. This process, known as thermal energy storage, captures waste heat generated during electricity production, which can be stored and converted back into electricity when demand spikes. During periods of low power demand, SMRs continue to operate at full capacity, with surplus heat being stored for later use. When demand increases, this stored heat is then converted back into electricity, ensuring a steady, uninterrupted power supply, thus making the power generated from SMRs scalable.
Despite these advantages, the development and deployment of SMRs are not without challenges. The technological innovations introduced with SMRs come with their own set of difficulties, such as the handling and disposal of spent nuclear fuel. Furthermore, the commercial viability of SMRs will largely depend on achieving economies of scale in manufacturing and widespread market acceptance.
In conclusion, SMRs present a promising pathway for the evolution of the nuclear energy industry. By addressing long-standing challenges and introducing new possibilities, SMRs are set to play a pivotal role in the future energy mix. As we strive to meet our energy demands in a sustainable and efficient manner, the development and deployment of SMRs could represent a significant step toward realizing this goal.
ADI Analytics is a prestigious, boutique consulting firm specializing in oil & gas, energy transition, and chemicals since 2009. We bring deep, first-rate expertise in a broad range of markets including sustainable energies, where we support Fortune 500, mid-sized and early-stage companies, and investors with consulting services, research reports, and data and analytics, with the goal of delivering actionable outcomes to help our clients achieve tangible results.
We also host the ADI Forum, one of Houston’s distinguished industry conferences, to bring c-suite executives from oil & gas, energy transition, and chemicals together for meaningful dialogue and strategic insights across the value chains.
Subscribe to our newsletter or contact us to learn more.
– Ninad Kulkarni



















