
Cement, a fundamental building block of modern construction, has long been integral to the development of infrastructure worldwide. Today, concrete made from cement is the most consumed material after water. However, its vital role comes at a significant environmental cost.
The production of traditional cement, also known as Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is highly energy and carbon intensive, responsible for 7-8% of global CO2 emissions, today. From mining raw materials in the quarry to production of clinker, an intermediate product in the kiln and final cement production, the entire process emits ̴ 900-950 kg of CO2 per ton of cement produced, with the clinker production step having the highest amount of emissions. Exhibit 1 indicates CO2 emissions across the cement production value chain.
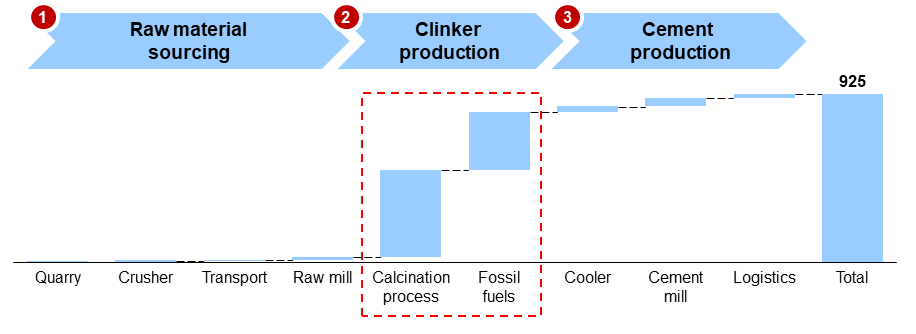
Exhibit 1. CO2 emissions across different cement production stages.
ADI expects rising population and economic growth, expanding infrastructure, and rising globalization to drive global cement demand. Global cement production may reach ̴ 4.2 billion tons by 2035 from 4.1 billion tons today, resulting in ̴ 4.0 gigatons of CO2 emission in business as usual (BAU) scenario. Due to the sheer volume and high emission intensity, cement production process possesses a significant challenge to achieving various climate goals.
Regulatory policies, technology development, and corporate commitments will drive CO2 emissions down via low-carbon and green cement. Governments worldwide are taking steps to include cement industry in cap-and-trade programs, aligning with other emission-intensive industries, thereby restricting emissions from cement production. Simultaneously, there is a push to incentivize and fund research and development focused on low-carbon and green cement alternatives. Several large cement producers around the world have also made various commitments towards decarbonization. Exhibit 2 shows CO2 % reduction targets set by major cement producers.
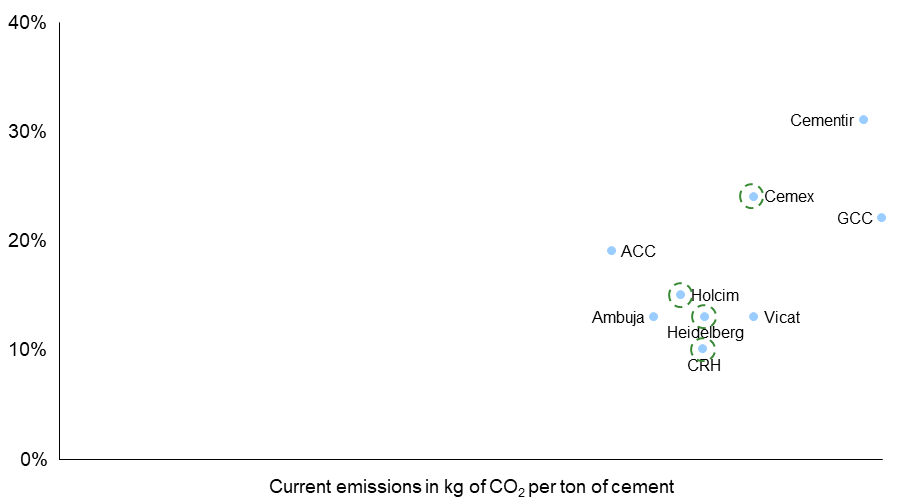
Exhibit 2. CO2 reduction targets for 2030 set by major cement producers.
There are several pathways to decarbonize the cement industry, each promising varying degrees of CO2 abatement potential. We will discuss these pathways in part II of the blog.
ADI has recently published a multi-client study on the future of green and low-carbon cement which is available immediately to help stakeholders access this dynamic space. Download the study prospectus here >>
ADI Analytics is a prestigious, boutique consulting firm specializing in oil & gas, energy transition, and chemicals since 2009. We bring deep, first-rate expertise in a broad range of markets including emission intensive industries, where we support Fortune 500, mid-sized and early-stage companies, and investors with consulting services, research reports, and data and analytics, with the goal of delivering actionable outcomes to help our clients achieve tangible results.
We also host the ADI Forum, one of Houston’s distinguished industry conferences, to bring c-suite executives from oil & gas, energy transition, and chemicals together for meaningful dialogue and strategic insights across the value chains.
Subscribe to our newsletter or contact us to learn more.
Pranav Laxpati



















